With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation funded during 2014-2015, Dr. Frank Kooy and colleagues at the University of Antwerp are conducting a double blind crossover trial of ganaxolone in patients with Fragile X syndrome. Results of this study were mixed (see Marinus: Results from Phase 2 Exploratory Clinical Study Support Continued Development of Ganaxolone in Fragile X Syndrome.)
Read moreResearch
Neural Markers of Fragile X: A Powerful New Tool for Clinical Trials
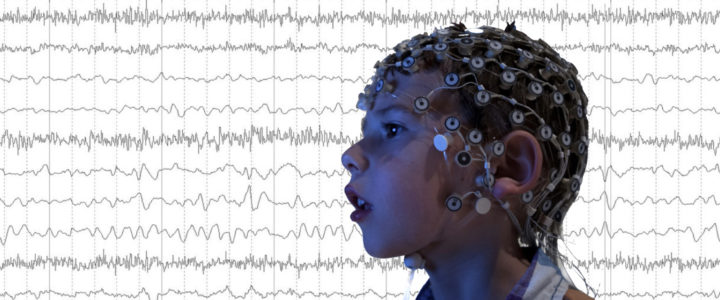
Once the neural marker is identified for a particular challenge, such as kids with poor language versus good language, neural markers can be measured during drug and behavioral therapy trials to see if a child is improving based on objective biological measures.
Read moreTargeting Serotonin Receptors to Treat Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation awarded in 2017, Dr. Clinton Canal targets seratonin receptors. “There are 15 unique serotonin receptors (at least) and many of them impact the function of brain circuits that are impaired in neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders,” said Dr. Canal. “Results from this project could guide new drug discovery or drug repurposing for Fragile X.”
Read morePreclinical Testing of Sleep-Wake Patterns as an Outcome Measure for Fragile X

FRAXA Research Foundation awarded $122,000 over 2016-2018 to Dr. Cara Westmark at the University of Wisconsin at Madison for studies of sleep disorders in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreMetformin, Diabetes Drug, Potential Fragile X Treatment

“We treated mice with metformin and corrected all the core Fragile X deficits. We are optimistic about using metformin in human clinical trials. This is a generic drug with few side effects” says Nahum Sonenberg, PhD, James McGill Professor, Department of Biochemistry, McGill Cancer Center, McGill University.
Read moreWhich is the right FMRP for Therapeutic Development of Fragile X Syndrome?

With a 2-year, $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2016-17, Dr. Samie Jaffrey at Weill Medical College of Cornell University explored which FMRP isoform is the best target to treat Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreBiomarker Discovery and Validation for Fragile X Syndrome

With a $120,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2015-2016, Dr. Eric Klann of New York University investigated potential new biomarkers in Fragile X syndrome and how to translate these markers from mouse models to human patients.
Read moreFragile X Nervous (System) Breakdown

“The occurrence and development of events by chance in a happy or beneficial way.” That’s how Lynne E. Maquat, PhD, describes the process of how her research extended to Fragile X syndrome to better understand it and ultimately find advanced treatments.
Read moreRepurposing Available Drugs to Treat Fragile X Syndrome – FRAXA Initiatives
FRAXA Research Foundation was founded in 1994 to fund biomedical research aimed at finding a cure for Fragile X syndrome and, ultimately, autism. We prioritize translational research with the potential to lead to improved treatments for Fragile X in the near term. Our early efforts involved supporting a great deal of basic neuroscience to understand the cause of Fragile X. By 1996, these efforts had already begun to yield results useful for drug repurposing. To date, FRAXA has funded well over $25 million in research, with over $3 million of that for repurposing existing drugs for Fragile X.
Read moreFragile X Research Tackles High Anxiety – Peter Vanderklish

Yes, we all know the signs of Fragile X anxiety: Ears begin turning red followed by incessant pacing, heavy breathing, stiffening body, flapping, jumping, avoidance or yelling. Sometimes, it’s the more severe screaming, pinching, scratching, biting and general tearing things up or, worse, the nuclear meltdown.
Read morePIKE as a Central Regulator of Synaptic Dysfunction in Fragile X Syndrome

With $255,000 from FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Suzanne Zukin at Albert Einstein College of Medicine studied signalling pathways in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreA Kinase Assay as a Biomarker for Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2017-2018, Dr. Frank Kooy at the University of Antwerp, Belgium, is investigating whether phosphorylation abnormalities are a suitable biomarker for the Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreUniversity of Cambridge Startup Healx is Rapidly Identifying Existing Drugs to Help Fragile X Patients

FRAXA awarded $44,000 to Healx in 2017 for drug repurposing to find new treatments for Fragile X syndrome. The results of this study include eight top “hits” which show promise for Fragile X. FRAXA is further investigating these hits.
Read moreTrial and No Error: Better Outcomes for Clinical Trials in Fragile X Syndrome

Johns Hopkins researcher Christina Timmerman, PhD, searches for a less subjective method to determine if a drug is working in patients with Fragile X syndrome. Many parents of children with Fragile X syndrome were crushed when promising drug trials were unexpectedly stopped a few years ago because subjective behavior-based outcome measures did not justify continuing the trials. The strong feelings linger today. If all goes well with Christina Timmerman’s research, future drug trials may be able to continue with additional metrics for assessment, until there are advanced treatments or even a cure for Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreFunction of FMRP and Test of a Novel Therapeutic Approach in a Fragile X Mouse Model

With a 2015-2016 $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Herve Moine and Dr. Andrea Geoffroy aim to uncover the exact role of FMRP and to test a novel possible means to correct for FMRP absence in the mouse model of Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreCorrecting Defects in Astrocyte Signaling in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from the FRAXA Research Foundation from 2015-2016, Dr. Laurie Doering and Dr. Angela Scott at McMasters University studied astrocytes in Fragile X. Astrocytes, brain cells which support neurons, do not transmit signals. Several treatment strategies for Fragile X have been proposed based on correction of “astrocyte phenotypes”.
Read moreSensory Hypersensibility in Fragile X Syndrome and BK Channel Openers
With $366,100 in grants from FRAXA Research Foundation, these investigators at the University of Orleans studied sensory abnormalities in Fragile X mice and test the ability of a class of drugs, BK channel openers, to rescue these abnormalities.
Read moreFragile X Mutant Mouse Models

With $375,000 in grants from the FRAXA Research Foundation since 2009, Dr. David Nelson has developed an impressive array of advanced mouse models of Fragile X, at Baylor College of Medicine. These models are available to investigators worldwide on request. This resource has been essential for a broad, rapid distribution of Fragile X and related gene mouse models and has increased the pace of Fragile X research.
Read moreMicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation in 2015-2016, Dr. Mollie Meffert and Dr. Christina Timmerman at Johns Hopkins University studied groups of small RNAs, known as microRNAs, which are greatly decreased in brain tissue of Fragile X mice vs. normal controls.
Read moreRepurposing Drugs to Dampen Hyperactive Nonsense-Mediated Decay in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from the FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Lynne Maquat and Dr. Tatsuaki Kurosaki will investigate nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in Fragile X. NMD is a “housekeeping” process that cells use to prevent faulty proteins from being made. But there is too much of it in Fragile X syndrome. There are already available drugs that suppress NMD – including caffeine.
Read moreAltered Sleep in Fragile X Syndrome: Basis for a Potential Therapeutic Target

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2016-2018, Dr. Carolyn B. Smith and Dr. Rache Sare at the National Institute of Mental Health investigated the basis of sleep problems in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreEnhancement of NMDA Receptor Signaling for the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome

FRAXA Research Foundation funded a 2016-2017 Fellowship for Dr. Stephanie Barnes in the University of Edinburgh lab of Dr. Emily Osterweil. With this $90,000 award, the team is investigating NMDA signaling in fragile X syndrome mice.
Read moreIdentifying Biomarkers for Fragile X Syndrome – A Study in Argentina

Bio·mark·er, noun, a distinctive biological or biologically derived indicator of a process, event, or condition. Doesn’t help? Well, it’s perfectly clear to Argentinian researchers Patricia Cogram, PhD, and Paulina Carullo, MD, from the FLENI Institute in Buenos Aires, Argentina. They understand there is an urgent need for validated biomarkers after recent Fragile X syndrome clinical trials have failed on their primary endpoints.
Read moreDouble Down: Fragile X Clinical Trial Combines Two Available Drugs
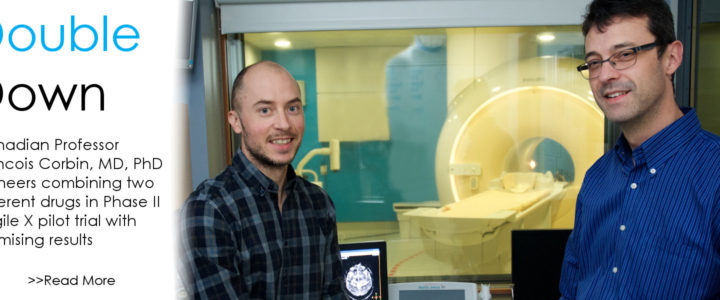
If all the science world’s a stage, Fragile X researchers are more than merely players. They are center stage. So believes Francois Corbin, MD, PhD, professor, Université de Sherbrooke, Canada, who directs the university’s Fragile X Clinic. Corbin, who has received more than $100,000 in FRAXA support since 2012, is leading a pilot randomized Phase II trial, exploring the tolerability and the synergistic effect of a combined therapy.
Read moreThe X Factor – Turning on X Chromosome Genes to Treat X-linked Disorders

Harvard researcher Jeannie T. Lee, MD, PhD, moves closer to turning on select genes on the X chromosome to treat people with X-linked disorders.
Read more
