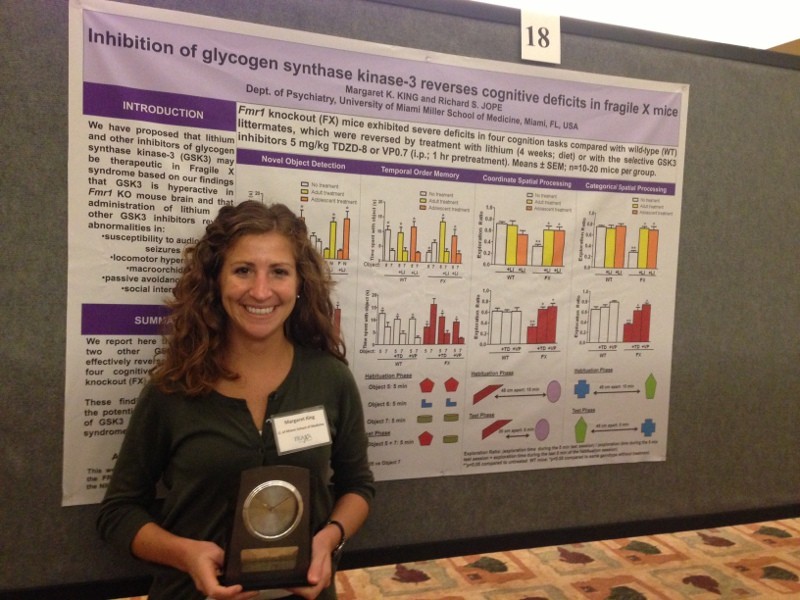
Targeting AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Fragile X Syndrome
With this grant from FRAXA, Dr. Peter Vanderklish explored AMPK activators to treat Fragile X. Both metformin and resveratrol, found in red wine, are AMPK activators.
Fruit Flies to Model and Test Fragile X Treatments
Boosting cAMP signaling restores memory and fixes brain-signaling defects in Fragile X models, suggesting diabetes drugs like metformin may help.
Analysis of Developmental Brain Dysfunction in Families
No strong behavioral similarities were found between parents and children with Fragile X, indicating family history may not guide clinical trial recruitment.
Crossroads of Fragile X and Alzheimers Research
Last week researchers at VIB Leuven in Belgium published evidence that a brain pathway involving the protein APP (Amyloid Precursor Protein) plays a vital role in development of Fragile X syndrome, one of the most common causes of autism. Scientists led by Dr. Emanuela Pasciuto in the laboratory of Prof Claudia Bagni published findings of their study in the journal Neuron.
Fragile X: Past, Present, Future – Video
A Fragile X presentation was given by Michael Tranfaglia, MD, FRAXA Medical Director at the IDD-C conference at Stanford University on April 21, 2015. This was an in-depth discussion of how research has brought us to the point of clinical trials, the problems encountered in recent trials, and where we go from here. Dr. Tranfaglia presents new ideas on Fragile X disease mechanisms and new treatment strategies which may address these.
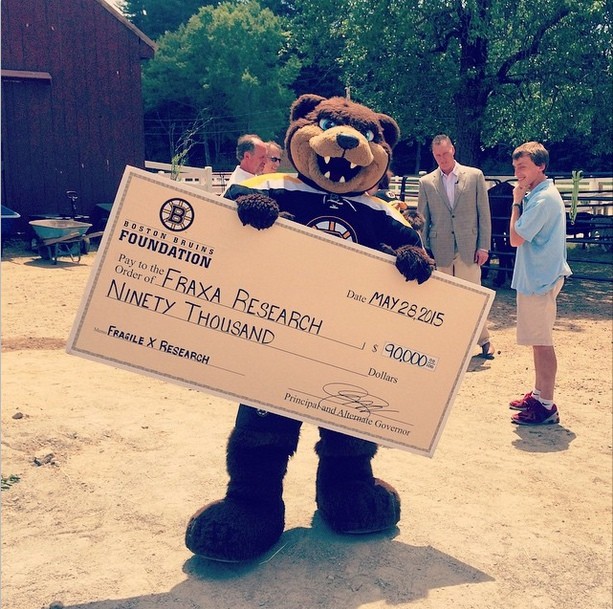
Boston Bruins Grant Funds New Fragile X Research
The Bruins Foundation pledged $90K to FRAXA, funding new Fragile X research at Gateway Farm in Merrimac, MA.
Boston Globe, “Playing a part in finding cure for Fragile X”
Fragile X is rare and not as highly publicized as many other better-known genetic diseases that attract media interest and generate richer revenue streams of giving. The world of the ailing doesn’t prioritize. There is no Find Help 101 manual for funding charities or what makes the public wake up one day and pour out its heart, empty its wallet, join a bike-a-thon for its cure.
Fragile X Treatment: New Research Directions
In the wake of negative results from several high-profile clinical trials in Fragile X, we find ourselves questioning many of our previous assumptions about the nature of this disorder. After all, understanding the basic pathology of disease is critical to development of new treatments — this is true across the board, in all branches of medicine.
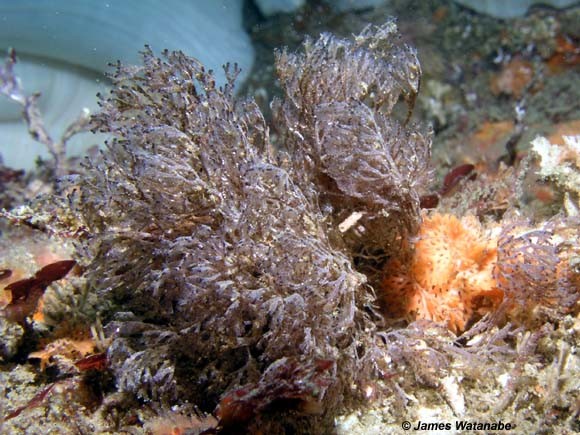
Bryostatin Restores Learning and Memory in Adult Fragile X Mice
A bizarre marine critter found off the California coast — Bugula neritina— is the only known source of a potential new Fragile X treatment, Bryostatin. Last month, FRAXA sat down with scientists from Neurotrope BioScience, a specialty biopharmaceutical company developing medicines for rare diseases and Alzheimer’s based on Bryostatin. Their Fragile X program is based on research by a West Virginia team led by Daniel Alkon, MD, which showed that Bryostatin-1 restores hippocampal synapses and spatial learning and memory in adult Fragile X mice.
Fragile X Programs at UMASS – University of MA, Worcester
Fragile X Syndrome Behavioral Health Clinic The Center for Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders (CANDO) is opening a specialty clinic for individuals with Fragile X Syndrome (under the direction of Dr. Jean Frazier) to evaluate and provide treatment for behavioral challenges.
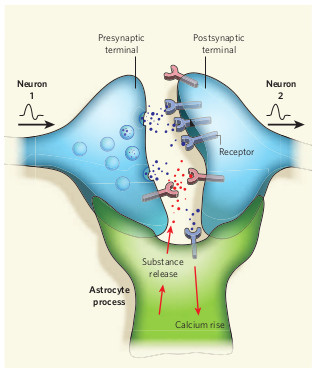
The Endocannabinoid System in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
Fragile X disrupts endocannabinoid signaling. This study in mice demonstrated that correcting it may calm brain hyperexcitability and improve symptoms.
Inhibitors of STEP as a Novel Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome
STEP inhibition reversed behavioral and synaptic Fragile X deficits in mice (Neuropharmacology, 2018), highlighting STEP as a promising treatment target.
Molecular Mechanisms of Cytoskeletal Regulation by FMRP
With FRAXA funding, Dr. Jaffrey linked FMR1 loss to abnormal dendritic spines via RhoA signaling, suggesting RhoA-targeted therapies could help treat Fragile X.
Students at WPI helping FRAXA Research Foundation
Two WPI student teams are working with FRAXA to improve our website and create a mobile app as part of their Interactive Qualifying Project.
NPR, “A Family’s Long Search For Fragile X Drug Finds Frustration, Hope”
There is no effective treatment for the rare genetic disorder Fragile X syndrome, so two parents created a foundation to fund research. But they found there’s no easy road to a cure. For a few weeks last year, Michael Tranfaglia and Katie Clapp saw a remarkable change in their son, Andy…
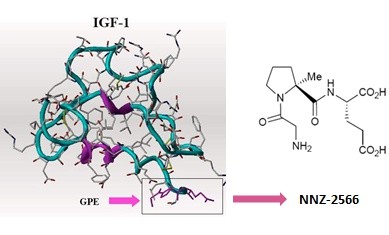
Neuren’s NNZ-2566 Shows Clinical Benefit in Rett Syndrome Trial
This isn’t a Fragile X trial, but the Neuren compound, NNZ-2566, that is in trials now for Fragile X has shown significant positive effects in a Phase 2 trial for Rett syndrome. The results of the trial are interesting, in that improvement was seen a Rett syndrome-specific rating scale compared to placebo, and there was also improvement noted on the CGI-I (Clinical Global Impression of Improvement) and Caregiver Top 3 Concerns. However, there was no effect seen on ABC scores (Aberrant Behavior Checklist) compared to placebo. Many in the Fragile X field have noted the inadequacies of the ABC; indeed, it was never designed or intended to be an outcome measure for clinical trials.
Clinical Trials Outcome Measures
There is a critical need for reliable biomarkers and clinical outcome measures for Fragile X syndrome. Treatment trials depend on this.
NIH Awards $35 Million to Three Fragile X Research Teams
NIH is investing $35M in three Fragile X Research Centers. All teams have been funded by FRAXA and will now receive over $2M annually for five years.
Targeting the Endocannabinoid System in Adult Fragile X Mice
CB1 blockade with rimonabant reversed cognitive, sensory, and seizure symptoms in FXS mice, highlighting the endocannabinoid system as a therapeutic target.
Channelopathies: Altered Ion Channels in Fragile X Syndrome
Ion channel defects (“channelopathies”) in Fragile X disrupt neuron firing and network balance. This study maps these channel changes to guide targeted treatments.
Phase 1 Clinical Trial of Mega Green Tea Extract in Fragile X Syndrome
An early trial of green tea extract EGCG improved cognition in Fragile X. It targets ERβ and reduces overactive PI3K/mTOR/ERK signaling linked to FXS symptoms.
Functional Interplay Between FMRP and CDK5 Signaling
FRAXA-funded work showed CDK5 signaling is disrupted in Fragile X. CDK5 drugs are in development for Alzheimer’s so this pathway offers a promising new FX treatment angle.
Computational Analysis of Neural Circuit Disruption in Fragile X Model Mice
FRAXA-funded researchers used advanced computer models to uncover how FXS brain circuits change and predict which treatments may correct them. Results published.
Synaptic Characterization of Human Fragile X Neurons
Stanford scientists used human stem-cell–derived neurons to show that retinoic acid signaling is blocked by Fragile X, revealing a new pathway to target for treatment.