Tetra Discovery Partners Initiates Phase 2 Trial of BPN14770 in Fragile X Syndrome
This 2-Period Crossover Study of BPN14770 is accepting adults males with Fragile X syndrome at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago. Principal Investigator of the study is Elizabeth Berry-Kravis, MD, PhD.
A selective inhibitor of the phosphodiesterase type-4D (PDE4D), BPN14770 has shown the ability to improve the quality of connections between neurons and to improve multiple behavioral outcomes in the Fragile X mouse model.
Pharmacological Tolerance in the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome
FRAXA funded MIT work to probe tolerance to key Fragile X drugs, including mGluR5 inhibitors and arbaclofen, and to identify ways to sustain long-term treatment benefits.
FRAXA Research Grants Drive Big Investments in Fragile X
Most people know that FRAXA supports academic research at many institutions such as Harvard University, University of Pennsylvania, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Yale University. However, FRAXA is also working with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies around the world. Mike spends a lot of his time advising and collaborating with industry partners.
Newly Discovered Regulatory Pathways in Fragile X
Studies at Yale University and elsewhere are showing that FMRP plays a significant role in the regulation of potassium channels. Looking forward, potassium channel opener drugs could rescue some symptoms of Fragile X in humans.
Drug Repurposing Study Results Accelerate Progress Towards Fragile X Treatments
While there are over 8,000 rare diseases affecting an estimated 350 million people worldwide, only around 200 of these conditions have effective treatments. Due to the high cost of developing new drugs, rare diseases have historically been less attractive to pharmaceutical companies. Drug repurposing systematically leverages the detailed information available on approved drugs and reduces the time and money needed to deliver safe “new” treatments, but with greater success rates and a potentially more immediate impact on health care.
Clinical Trial of Ganaxolone in Patients with Fragile X Syndrome
Dr. Frank Kooy and colleagues conducted a double blind crossover trial of ganaxolone in patients with Fragile X with FRAXA funding. Results of this study were mixed.
Neural Markers of Fragile X: A Powerful New Tool for Clinical Trials
Once the neural marker is identified for a particular challenge, such as kids with poor language versus good language, neural markers can be measured during drug and behavioral therapy trials to see if a child is improving based on objective biological measures.
Preclinical Testing of Sleep-Wake Patterns as an Outcome Measure for Fragile X
FRAXA Research Foundation awarded $122,000 to Dr. Cara Westmark at the University of Wisconsin at Madison for studies of sleep disorders in Fragile X syndrome.
Can STEP Inhibitors Treat Fragile X Syndrome? Yale Professor Investigates
Yale Professor Paul Lombroso, MD, is testing STEP inhibitors to improve cognitive and social behaviors in those affected by Fragile X syndrome.
Fragile X Treatment: New Research Directions
In the wake of negative results from several high-profile clinical trials in Fragile X, we find ourselves questioning many of our previous assumptions about the nature of this disorder. After all, understanding the basic pathology of disease is critical to development of new treatments — this is true across the board, in all branches of medicine.
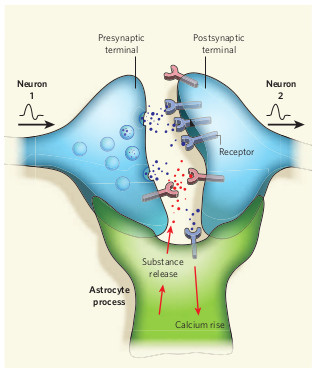
The Endocannabinoid System in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
Fragile X disrupts endocannabinoid signaling. This study in mice demonstrated that correcting it may calm brain hyperexcitability and improve symptoms.
Inhibitors of STEP as a Novel Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome
STEP inhibition reversed behavioral and synaptic Fragile X deficits in mice (Neuropharmacology, 2018), highlighting STEP as a promising treatment target.
NIH Awards $35 Million to Three Fragile X Research Teams
NIH is investing $35M in three Fragile X Research Centers. All teams have been funded by FRAXA and will now receive over $2M annually for five years.
Seizures in Fragile X Syndrome and Therapeutic Potential of NMDA Receptor Antagonists
Dr. Wong studies how NMDA and mGluR receptors interact to trigger seizures in Fragile X, revealing NR2B-specific blockers as a promising targeted treatment.
Potassium Channel Modulators to Treat Fragile X
FRAXA-backed Yale discoveries tied Fragile X to Kv3.1/Slack channel defects—leading to a partnership with Autifony to develop targeted treatments.
Preclinical Evaluation of Serotonin Receptor Agonists as Novel Pharmacological Tools in Fragile X Syndrome
With FRAXA funding the team found that activating 5-HT7 receptors reversed excess mGluR-LTD in Fragile X mice, pointing to a new route to fix synapses.
Ab-Mediated Translation in Fragile X Syndrome
This work found amyloid precursor protein (APP) overexpression and increased β-amyloid in Fragile X mice, implicating Alzheimer-related pathways in FXS pathology.
Inherited Channelopathies in Cortical Circuits of Fmr1 KO Mice
Researchers found that Fragile X brain circuits show faulty ion channel activity (channelopathies). Fixing these channels may restore normal brain signalling.
Using Fenobam to Reduce APP and Abeta in Fragile X Mice
With FRAXA funding, Drs. James Malter and Cara Westmark studied how APP and its metabolite may drive excess protein synthesis in Fragile X, aiming to restore balance.
Taurine and Somatostatin as Potential Treatments for Fragile X Syndrome: A Unifying Neuro-Endocrine Hypothesis
Dr. Abdeslem El Idrissi’s FRAXA-funded study tested somatostatin and taurine in Fragile X mice, revealing taurine’s promise as an accessible therapy.
Decreased Excitatory Drive onto Parvalbumin-Positive Neocortical Inhibitory Neurons in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
Drs. Jay Gibson and Kimberly Huber used FRAXA funding to uncover whether disrupted brain inhibition drives Fragile X, paving the way for targeted therapies.
Electrophysiological, Biochemical and Immunohistochemical Characterization of Kv3.1 in Auditory Brainstem Nuclei in the Fragile X Knockout Mouse
Dr. Leonard Kaczmarek’s Yale lab revealed how Fragile X disrupts potassium channels, impairing auditory processing and fueling sensory overload.