Join Dr. Tsai and Dr. Kumar on a journey into novel treatment avenues for Fragile X syndrome. Learn how activating mGluR7 could be a game-changer, opening up uncharted therapeutic territory.
Read morehypersensitivity
Astrocyte Contribution to Sensory Hypersensitivity in Fragile X Syndrome

Most Fragile X research has focused on one type of brain cells: neurons. But mounting evidence point to problems with astrocytes, star-shaped cells which are vitally important to normal brain function. This team is working to understand how astrocytes are involved in Fragile X and develop treatment approaches that targets astrocytes alone.
Read moremRNA Therapy for Fragile X Syndrome
Dr. Kathryn Whitehead, Associate Professor at Carnegie Mellon University, helped develop the revolutionary science behind the COVID-19 vaccines. With a $103,000 grant from FRAXA, her team will now adapt this technology to deliver the missing Fragile X protein, to treat people who have Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreCannabinoids as a Treatment for Fragile X Syndrome

Many people with Fragile X syndrome are hyper-sensitive to sights and sounds, and Electroencephalography (EEG) studies show that there are abnormalities in brain circuits. EEG studies show similar changes in Fragile X mice. So the team will use EEG tests in mice to find which drugs best reduce hypersensitivity. They can then easily move on to human EEG-based clinical trials. What they learn will tell us much more about why people with Fragile X are hypersensitive – and which drugs could best help them.
Read moreAuditory Dysfunction in Fragile X Syndrome in a Mouse Model of Fragile X

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA, Dr. McCullagh and Dr. Achem Klug at the University of Colorado investigated whether auditory neural circuits are altered in Fragile X mice. They saw minor differences in these mice compared to B6 (control) mice in several measures of auditory acuity. Fmr1 mice had increased latency to the startle response for almost all conditions compared to B6 mice, suggesting altered timing to acoustic cues. These experiments show that, consistent with patient reports and anatomical/physiological data, the auditory system is altered in a mouse model of FXS, though with some potential compensation leading to a subtle behavioral impact.
Read moreInterrogate the Functions of FMRP in Brain Development Using Stem Cells

Dr. Xinyu Zhao of the Waisman Center and Department of Neuroscience at University of Wisconsin-Madison joins us in this seminar to present Interrogate the Functions of FMRP in Brain Development Using Stem Cells.
Read moreAuditory System Dysfunction and Drug Tolerance in the Fragile X Mouse

FRAXA Research Foundation has awarded $90,000 over 2019-2021 to principal investigator Dr. Jay Gibson and postdoctoral fellow Dr. Andrew Holley at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. They are investigating circuit mechanisms for auditory system dysfunction and drug tolerance in the Fragile X mouse model.
Read moreMechanisms and Biomarkers of Sensory Hypersensitivity in the fmr1 Knockout Mouse

In this Fragile X research webinar we hear from Devin K. Binder, MD, PhD, Professor, University of California at Riverside Medical School and Khaleel Razak, PhD, Professor, University of California at Riverside as they present about Mechanisms and Biomarkers of Sensory Hypersensitivity in the fmr1 Knockout Mouse.
Read moreAripiprazole (Abilify) in the Treatment of People with Fragile X: An Anecdotal Account

The aim of this article is to discuss the use of Abilify (generic name: aripiprazole) as a treatment for people with Fragile X syndrome (FXS). As an “off-label” prescription, Abilify targets behaviors such as irritability, aggression, self-injury and severe tantrums.
Read moreScientists Find a New Way to Reverse Symptoms of Fragile X
FRAXA Investigator and MIT Professor Mark Bear and his colleagues have identified a valuable new target for Fragile X therapeutics: GSK3 alpha. Several FRAXA research teams previously identified GSK3 beta as a treatment target for Fragile X. The catch is that, so far, GSK3 beta inhibitors have proven too toxic for regular use. Dr. Bear’s new discovery opens up the possibility of developing more selective compounds with less toxicity and fewer side effects. Interestingly, lithium inhibits both GSK3 versions – alpha and beta.
Read moreResults Reported: Using EEG Responses to Sound for Fragile X Drug Discovery

Jonathan Lovelace, a FRAXA funded Postdoc at UC Riverside, has made some exciting EEG findings over the past few years studying auditory hypersensitivity in mice and therapeutic drug treatments. A big obstacle in FXS research has been establishing reliable, unbiased, and translation relevant biomarkers that can be used to determine the effectiveness of therapies. One of the most important discoveries they have made is the striking similarity in EEG biomarkers between mice and humans.
Read moreCorrecting Sensory Processing in Fragile X Mice by Modulating Kv3.1

FRAXA awarded a $90,000 grant to Carlos Portera-Cailliau, PhD and Nazim Kourdougli, PhD at UCLA to investigate whether a novel drug can rescue sensory processing deficits in Fragile X mice. People with Fragile X have similar problems in sensory processing. This new drug acts on Kv3.1, a promising Fragile X treatment target also being pursued by UK-based Autifony Therapeutics based on FRAXA-funded research done at Yale.
Read moreNovel Modulators of Potassium Channels to Treat Fragile X

With funding from FRAXA over 2015-2017, the Yale University team of Leonard Kaczmarek, PhD showed that the firing patterns of auditory neurons in response to repeated stimulation is severely abnormal in Fragile X mice. Based on these results, they are collaborating with the UK-based company Autifony to develop advanced compounds which may reverse these deficits.
Read moreNKCC1 Inhibitor Bumetanide Corrects Synaptic and Circuit Hyperexcitability in Fragile X Mouse Model

With $258,000 in grants since 2013 from FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Anis Contractor and Dr. Qionger He at Northwestern University are exploring the potential of the available drug bumetanide to correct altered GABA signalling in a mouse model of Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreUnderstanding and Reversing Hypersensitivity to Sounds in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2018-2019, Drs. Devin Binder, Iryna Ethell, and Patricia Pirbhoy at the University of California at Riverside aim to understand – and reverse – hypersensitivity to sound in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreNewly Discovered Regulatory Pathways in Fragile X

Studies at Yale University and elsewhere are showing that FMRP plays a significant role in the regulation of potassium channels. Looking forward, potassium channel opener drugs could rescue some symptoms of Fragile X in humans.
Read moreIn Their Own Words: Reports From the International Fragile X Workshop

The 18th International Fragile X and Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Workshop in Quebec, Canada, was a great success, featuring Fragile X much more heavily than any previous meeting in this series! We asked our speakers to summarize their work in their own words, with brief updates from researchers investigating Fragile X.
Read moreCombinatorial Drug Treatment in a Model of Fragile X Syndrome using Novel Biomarkers

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation awarded over 2016-2017, University of California researchers Khaleel Razak, PhD, and Jonathan W. Lovelace, PhD, are exploring drug combinations to limit hypersensitivity to sounds in Fragile X mice.
Read moreNeural Markers of Fragile X: A Powerful New Tool for Clinical Trials
Once the neural marker is identified for a particular challenge, such as kids with poor language versus good language, neural markers can be measured during drug and behavioral therapy trials to see if a child is improving based on objective biological measures.
Read moreRepurposing Available Drugs to Treat Fragile X Syndrome – FRAXA Initiatives
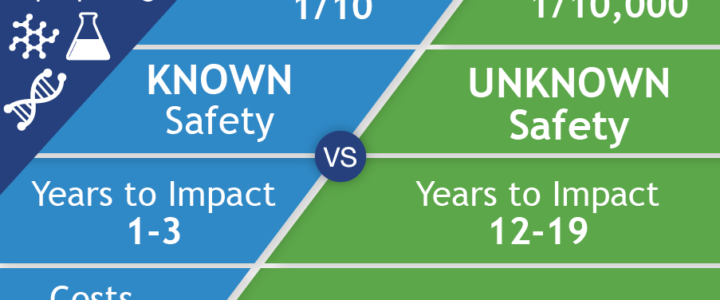
FRAXA Research Foundation was founded in 1994 to fund biomedical research aimed at finding a cure for Fragile X syndrome and, ultimately, autism. We prioritize translational research with the potential to lead to improved treatments for Fragile X in the near term. Our early efforts involved supporting a great deal of basic neuroscience to understand the cause of Fragile X. By 1996, these efforts had already begun to yield results useful for drug repurposing. To date, FRAXA has funded well over $25 million in research, with over $3 million of that for repurposing existing drugs for Fragile X.
Read moreFragile X Research Tackles High Anxiety – Peter Vanderklish

Yes, we all know the signs of Fragile X anxiety: Ears begin turning red followed by incessant pacing, heavy breathing, stiffening body, flapping, jumping, avoidance or yelling. Sometimes, it’s the more severe screaming, pinching, scratching, biting and general tearing things up or, worse, the nuclear meltdown.
Read moreKimberly Huber, PhD, Explores Hyperexcitability in Fragile X Syndrome

Ever wonder why your child with Fragile X suddenly screams for no apparent reason or jumps and flaps uncontrollably seemingly for hours? You got it: hyperexcitability. But what exactly causes it? And what can fix it? Kimberly Huber, PhD, is working long and hard in her lab to answer those questions. Dr. Huber, professor, Neuroscience, UT Southwestern Medical Center, is seeking to understand how FMRP regulates connections between brain cells, called synapses, and the function of brain circuits, which are several connected brain cells.
Read moreMeltdown no more? Targeting Hypersensitivity in Fragile X

We’ve all been there. Our child with Fragile X hears something and becomes excited. Very excited. Hand flapping follows with non-stop jumping and ear-piercing squawking. Nothing helps. No meds. No iPhone. No magic toy. Several minutes go by. Sometimes longer. How many times have you apologized in a grocery store — or restaurant — or at the mall? Wouldn’t it make our lives better if this unpredictable excitability was minimalized or eliminated? That’s the premise behind research being conducted at University of California, Riverside. Principal Investigator Khaleel Razak, PhD, and postdoctoral fellow Jonathan W. Lovelace, PhD, are studying mice genetically altered to mimic the genetic characteristics of humans with Fragile X Syndrome.
Read moreFragile X Cure One Step Closer with FRAXA Support of $1 Million in New Research

4 Countries – 10 Teams – $1 Million for finding new treatment targets, to pinpointing outcome measures for future clinical trials, to attempting to reactivate the gene which is silenced in Fragile X syndrome, these innovative scientists will bring us closer to a cure.
Read morePotassium Channel Modulators to Treat Fragile X

With $246,000 in funding from FRAXA over 2012-2014, the Yale University team of Leonard Kaczmarek, PhD, showed that loss of FMRP leads to an increased Kv3.1 potassium currents and decreased Slack potassium currents in neurons. Both of these changes impair timing of action potentials in auditory neurons (and likely others throughout the brain). The team also found that the firing pattern of neurons in response to repeated stimulation is severely abnormal in Fragile X mice. Based on these results, they are collaborating with the UK-based company Autifony to develop and test advanced compounds which may reverse these deficits.
Read more